Gum Surgery: An Overview
Gum surgery is a dental procedure performed to treat gum disease, improve gum aesthetics, or restore gum health. It is commonly recommended for individuals with periodontal disease (advanced gum disease), gum recession, or excessive gum tissue affecting their smile.
Types of Gum Surgery
- Gingivectomy – Removes excess gum tissue caused by gum overgrowth or infection.
- Gingivoplasty – Reshapes the gums for a more natural and aesthetic appearance.
- Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery) – Lifts the gums to remove deep plaque and tartar, then reattaches them securely to the teeth.
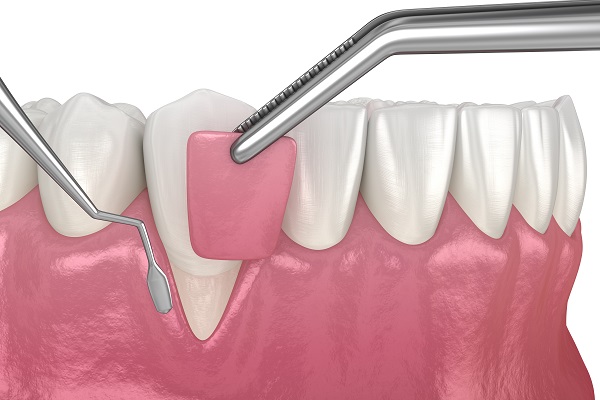
- Gum Graft Surgery – Uses tissue from another part of the mouth (or a donor source) to cover exposed tooth roots caused by gum recession.
- Crown Lengthening – Removes excess gum tissue to expose more of the tooth, often for cosmetic reasons or to prepare for a dental crown.
Benefits of Gum Surgery
✔ Treats and prevents further gum disease
✔ Reduces gum pockets and improves oral hygiene
✔ Restores gumline and prevents tooth sensitivity
✔ Enhances smile aesthetics
✔ Strengthens teeth by improving gum support
Gum Surgery Procedure
- Consultation & Diagnosis – A periodontist examines the gums and determines the appropriate surgical procedure.
- Anesthesia & Preparation – Local anesthesia is applied to ensure a pain-free experience.
- Surgical Treatment – The procedure is performed based on the patient’s needs (removing excess tissue, grafting, or reshaping gums).
- Healing & Recovery – Gums heal over a few weeks, with post-care instructions including soft foods, oral rinses, and gentle brushing.
Gum surgery is a highly effective treatment to restore oral health, prevent tooth loss, and enhance the appearance of the gums.